
Hitler proclaims the merging of the roles of Chancellor and President. Victims include Ernst Röhm (the Head of the SA) and other leading Nazis.Ģ nd August 1934: Death of President Hindenburg Hitler removes enemies of the party through a purge of critics. The Nazis and Catholic Church sign an agreement to leave each other alone.ģ0 th June 1934: Night of the Long Knives The official secret police of Nazi Germany is created by Hermann Göring.Ģ0 th July 1933: Concordat with the Catholic Church The SA are used to intimidate customers.Ģ6 th April 1933: Establishment of the Gestapo The Nazis organise a boycott of Jewish shops and businesses. The Enabling Act gives Hitler complete authority in Germany.ġ st April 1933: Boycott of Jewish shops and businesses The Nazis use the fire to pass a decree banning the Communist Party and suspending some civil liberties.Ģ3rd March 1933: The Enabling Act passes the Reichstag Hitler is appointed Chancellor by President Hindenburg.įire rips through the Reichstag building and Dutch Communist Van der Lubbe is arrested and executed for starting it.Ģ8 th February 1933: Reichstag Fire decree 37% of voters support Hitler and the Nazis.ģ0 th January 1933: Hitler appointed Chancellor The Nazis win 230 seats in the Reichstag election making them the largest party. The US Stock market crashes triggering events that lead to the Great Depression in the 1930s.ģ1 st July 1932: Nazis largest party in the Reichstag The Young Plan significantly reduces German reparations and gives Germany longer to pay them.ģ rd October 1929: Gustav Stresemann diesįormer Chancellor and Foreign Minister who helped the Weimar Republic recover, dies of a stroke. The Kellogg-Briand Pact binds nations into an agreement not to use war as a method of solving disputes.

This had been prohibited under the Treaty of Versailles.Ģ7 th August 1928: Kellogg-Briand Pact agreed Germany is admitted to the League of Nations. Hitler meets with leading Nazis to reorganize the party and cement his authority.Ĩ th September 1926: Germany joins the League of Nations
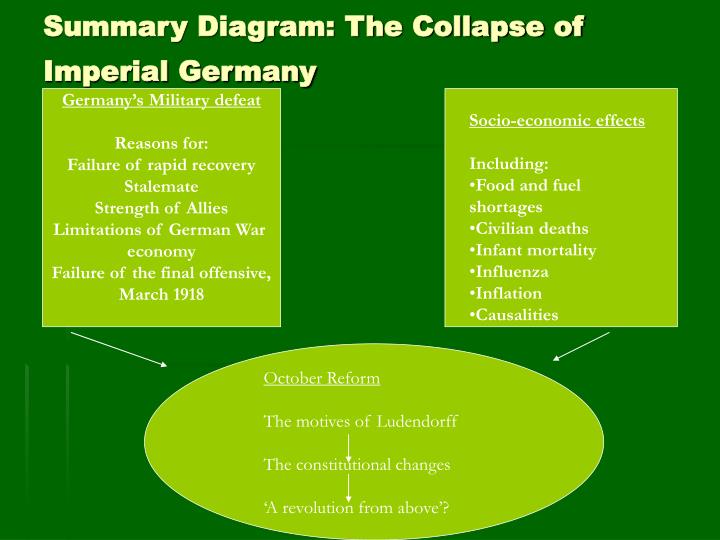
Germany agrees to the border set out in the Treaty of Versailles.ġ4 th February 1926: The Bamberg Conference Mein Kampf, Hitler’s book is published with his ideas for Germany. The agreement helps Germany with its reparations. Hitler is sent to Landsberg prison for his role in it. The Nazis attempt a failed putsch in Munich. Gustav Stresemann becomes Chancellor and Foreign Minister. The Reichsmark becomes worthless.ġ3 th August 1923: Stresemann becomes Chancellor and Foreign Minister Prices begin to rise rapidly made worse by the printing of money to pay striking workers in the Ruhr. A strike brings the Putsch to an end.ġ1 th January 1923: Occupation of the Ruhrįrench and Belgian troops occupy the Ruhr industrial region as Germany had stopped paying reparations. The Constitution of the Weimar Republic is signed and introduces much greater democracy.Ī revolt in Berlin led by Wolfgang Kapp supported by the Freikorps.

Germany signs the Treaty of Versailles - the peace treaty that ends the First World War.ġ1 th August 1919: The Weimar Constitution is signed Friedrich Ebert is elected President.Ģ8 th June 1919: Germany signs the Treaty of Versailles The first Assembly of the Weimar Republic is established and drafts the Constitution. The Freikorps suppress the rebellion.įebruary-June 1919: Weimar National Assembly established Leaders include Karl Liebknecht and Rosa Luxemburg. The Spartacist League hold an uprising in Berlin. Germany signs an armistice, bringing an end to the fighting.ĥ th-12 th January 1919: The Spartacist Uprising After several protests and a mutiny of German sailors in Kiel, he leaves Germany for the Netherlands.ġ1 th November 1918: The Armistice is signed The Emperor of Germany leaves after initially refusing to agree to surrender. Weimar and Nazi Germany (1918-39) Revision Guide for Edexcel GCSE Historyĩ th November 1918: Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicates his throne


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
